Gen Z characteristics (and why they matter in the workplace)
Understanding Gen Z characteristics is essential for any organisation recruiting, retaining or developing Generation Z employees. Born between 1997-2012, Gen Z brings seven distinct characteristics to the UK workplace that set them apart from Millennials, Gen X, and Boomers. These Gen Z characteristics aren't stereotypes—they're data-backed traits shaped by unique generational experiences including the 2008 financial crisis, 24/7 digital connectivity, and unprecedented economic uncertainty.
Want to see the Gen Z blogs in one place?
TL;DR:
Gen Z (born 1997-2012) now form over 20% of the UK workforce. They're the most well-behaved, diverse, and digitally native generation, shaped by the 2008 financial crisis and 24/7 online life. Success with Gen Z requires: clear communication, authentic values, regular feedback, personalised development, and collaborative opportunities. They're pragmatic, diligent, and value mental health - not snowflakes, but a generation with untapped potential.
Gen Z is the most important generational shift so far, but their experiences and outlook are not understood well enough by older generations. They are different from previous generations for good reason.
Generation Z's young adults have huge potential to meet the challenges of today. This blog also covers age ranges of generations including generation alpha.
New book! The Snowflake Myth: Explaining Gen Z in the workplace and beyond
CLICK HERE for a free chapter
Solutions to manage Gen Z employees effectively in the UK
Be clear, be thorough details how Gen Z has been bombarded by social media content from a young age, and how organisations can respond. Furthermore, Gen Z's responsibility to resolve issues like climate change has made them suspicious of older generations.
Be who you say you are focuses on the value of authenticity. It also describes how the battle to attract Gen Z can be won, and also that retaining the first generation of digital natives starts from the very beginning.
Regular & precise feedback concentrates on how older generations can support the professional development of Gen Z staff. They have been educated differently, and with a higher level of expectation. Employers who bring this to the workplace will reap the rewards.
Making professional development more personal focuses on the gap which has opened up between academic outcomes and personal skills for those of the same age. Hiring managers need to be aware on how they can close this gap.
Enable opportunities to contribute and collaborate looks at how organisations can make the most of gen z consumers habits in the workplace. Gen Z's propensity to engage is a lot more than older generations tend to envisage.
The 7 Key Gen Z Characteristics
Based on research and direct experience leading secondary schools full of Generation Z students, these are the defining Gen Z charactertics in the UK. If you want to understand Gen Z behaviour in the workplace you need to understand them.
Gen Z characteristics #1: Well-behaved: Gen Z is the most well-behaved age group so far. Previous generations lived their formative years differently. Older generations are rarely aware of this, and how it can help in the workplace.
Gen Z characteristics #2: Prudent - Prudent covers why generation z has good reason to be less confident about future economic security, even beyond the current cost of living crisis and recovery from the pandemic. This affects their choices are work and career.
Gen Z characteristics #3: Pragmatic - Gen Z is a pragmatic generation with a focus on work life balance, but also on side hustles. They have concerns about their long-term prospects, not least due to the impact of the pandemic.
Gen Z characteristics #4: Diligent - Diligent discusses why Gen Z's higher education outcomes are only one reason why they should not be characterised, or stereotyped, as slackers or snowflakes. The extent to which they will uphold their personal values about, for example, equality or work/life balance should not be conflated with a reluctance to work hard.
Gen Z characteristics #5: Apprehensive - Apprehensive refers to the mental health crisis amongst young people, and how employers can respond. These is where key differences with other generations are most obvious, particularly baby boomers. Gen Z expects this to be taken seriously, not doing so is a clear red line for many.
Gen Z characteristics #6: Diverse - Diverse discusses how generation z forms the most diverse generation to date. This is one key reason why the topic matters so much to them. Diversity is a broader topic than is often understood.
Gen Z characteristics #7: Patient - Patience is the one that my Gen X peers can find the hardest to understand. Yet in terms of key life milestones many Gen Zers are waiting longer than ever.
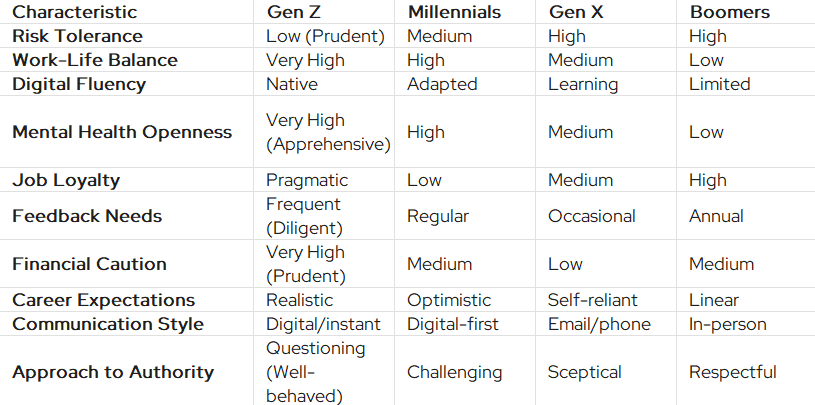
How Gen Z Characteristics Compare to Other Generations
Differences within generations are FAR bigger than those between. So this is highly generalised but still tells an interesting story.
Gen Z workplace videos
A video for each characteristic and solution, plus interview footage. All on my youtube channel.
Gen Z key characteristics
Gen Z solutions
Gen Z characteristics in the UK context
Generation Z forms over 20% of the UK workforce in 2025. In ten years time they will form the biggest group. These Gen Z characteristics manifest uniquely in British workplaces:
Global Financial Crash: It may have been in 2008 but it arrived as the oldest Gen Z started secondary school, cutting public services and low economic growth
Brexit Impact: UK Gen Z came of age during unprecedented political uncertainty, reinforcing their pragmatic and apprehensive characteristics
University Debt: UK Gen Z graduates carry average student loans of £45,000 (£15K in Scotland), intensifying their prudent financial behaviours
British Mental Health Services: NHS waiting times have particularly impacted Gen Z's apprehensive characteristic around mental health support
Understanding these UK-specific factors helps organisations tailor their Gen Z recruitment and retention strategies
Why Gen Z matters in today's workplace
Gen Z is the most important generational shift so far, but their experiences and outlook are not understood well enough by those who have come before them. Generation Z has huge, as yet mostly untapped, potential to meet the challenges of today.
It is a significant topic for me. Gen Z is the generation which attended the secondary schools I led from 2006 to 2018. In recent years I have seen them described in ways I did not recognise, or appreciate. More on that in the blogs.
Generation Z is approaching a quarter of the UK workforce. The older ones are already in management positions in large companies and ripping up the rulebook on their own. Their importance in the workplace will grow with every passing year.
Gen Z demographics and birth years (1997-2012)
Like every other generation, Generation Z is a social construct. It is not a feature of a birth certificate or a passport.
It is also representative of the speed of change over the last 100 years. History moves from talking about ‘ages’ (stone, bronze, iron) to ‘revolutions’ (agricultural, industrial) to ‘generations’ (Boomers, Generation X, Millennials, Generation Z) and so on.
Even within that we have moved from the names of generations created after a period of time has finished to ‘live’ naming (and also from generations naming themselves to being named by others). Fifteen years has become the standard amount of time to define a generation’s length.
These are not blunt cut-off points. For example, a younger Millennial born in 1994 is likely to have more in common with an older Gen Z born in 1997 than a Millennial born in 1982. The edges are blurry, and there is often much more variety within a generation than across them.
There is also a risk in analysing the differences between groups at different phases of life (i.e. those in their 20s vs 40s) rather than throughout their life (those born in mid 70s vs mid-90s).
Change does not impact everywhere at the same time at the same pace. As some were using bronze while others used iron, the same applies to generations. There is an argument that technology is harmonising some of this, and not always in a good way. There is a good case for saying it is a ‘western’ approach and thus limited.
But if the point needs to be made, the dialogue remains about human beings; generations may have some differences but they all belong to the same species. People should still be treated, managed and trained as individuals. Stereotyping is not helpful or relevant as we will see in particular with Gen Z.
What makes Gen Z different from Millennials?
In short, it is events which shape generations. Technological, political, economic and social events. Wars, stock market crashes, breakthroughs, attitudinal changes and so on. The Boomer generation started straight after the Second World War but it is not always so straight forward.
Over the course of the blogs I will explore in particular the differences between Millennials and Generation Z. They are not the same and the terms should not be used interchangeably.
A few of the main events which have affected each generation are listed here. It is a small selection and without a direct equivalent on each side.
The key is the impact that the event had on the generation, rather than it falling within the years of birth. This is not to say that 9/11 or social media only affected Millennials but that it had the most impact. Often it is because of their age at the time and the impact on their education and early professional life. These are not always easy arguments to make and are frequently tenuous.
Key events for Generation Z
Like every generation Gen Z has inherited the world left to them. They will make their own sense of it and form their own response. The impact of the Global Financial Crash in particular, and the austerity which followed was particularly significant as was the commercialisation of the internet.
Compared to the Millennials they have faced more difficult economic times, far more uncertainty and have had to deal with 24/7 reputation management online from an early age. All of this, and more, has significant implications for them in the workplace and their adult lives.
It is not all bad and, as outlined in this series, there are significant opportunities too for Generation Zs and those who work with them.
Frequently Asked Questions About Gen Z characteristics
What are the main Gen Z characteristics? The seven key Gen Z characteristics are: well-behaved, prudent, pragmatic, diligent, apprehensive, diverse, and patient. These characteristics distinguish Generation Z from Millennials and other generations in the workplace.
How do Gen Z characteristics affect workplace behaviour? As above, differences within generations are far bigger than differences between. Gen Z characteristics like pragmatism and prudence lead them to seek multiple income streams, while their diligent nature means they are arriving at the workplace with an academic record beyond any previous generation.
Are Gen Z characteristics the same in the UK as in the US? UK-specific factors like Brexit, university debt levels and NHS mental health service availability create distinct manifestations of these traits in British workplaces.
What's the difference between Gen Z and Millennial characteristics? As the table above indicates plenty of Gen Z characteristics are extensions of existing trends. Gen Z do not remember a time before the proliferation of smart phones and UK economic growth in their formative years was much weaker than for Millennials. But like any other generation they are not different species.
How can employers work with Gen Z characteristics effectively? Understanding Gen Z characteristics helps employers provide: clear expectations (well-behaved), financial security focus (prudent), clear career paths (pragmatic) and high quality learning opportunities (diligent).
Want to transform how your team works with Gen Z?
I deliver keynotes, masterclasses and workshops that turn these insights into actionable strategies your managers can use on Monday morning.